FOREX
The Forex market (forex, FX, or currency market) is a global decentralized market for the trading of currencies. In terms of volume of trading, it is by far the largest market in the world.The main participants in this market are the larger international banks. Financial centres around the world function as anchors of trading between a wide range of multiple types of buyers and sellers around the clock, with the exception of weekends. The foreign exchange market determines the relative values of different currencies.The foreign exchange market works through financial institutions, and it operates on several levels. Behind the scenes banks turn to a smaller number of financial firms known as “dealers,” who are actively involved in large quantities of foreign exchange trading. Most foreign exchange dealers are banks, so this behind-the-scenes market is sometimes called the “interbank market”, although a few insurance companies and other kinds of financial firms are involved. Trades between foreign exchange dealers can be very large, involving hundreds of millions of dollars. Because of the sovereignty issue when involving two currencies, Forex has little (if any) supervisory entity regulating its actions. The foreign exchange market assists international trade and investments by enabling currency conversion. For example, it permits a business in the United States to import goods from the European Union member states, especially Eurozone members, and pay Euros, even though its income is in United States dollars. It also supports direct speculation and evaluation relative to the value of currencies, and the carry trade, speculation based on the interest rate differential between two currencies.In a typical foreign exchange transaction, a party purchases some quantity of one currency by paying for some quantity of another currency. The modern foreign exchange market began forming during the 1970s after three decades of government restrictions on foreign exchange transactions (the Bretton Woods system of monetary management established the rules for commercial and financial relations among the world's major industrial states after World War II), when countries gradually switched to floating exchange rates from the previous exchange rate regime, which remained fixed as per the Bretton Woods system. The foreign exchange market is unique because of the following characteristics:its huge trading volume representing the largest asset class in the world leading to high liquidity; its geographical dispersion; its continuous operation: 24 hours a day except weekends, i.e., trading from 22:00 GMT on Sunday (Sydney) until 22:00 GMT Friday (New York); the variety of factors that affect exchange rates; the low margins of relative profit compared with other markets of fixed income; and the use of leverage to enhance profit and loss margins and with respect to account size. As such, it has been referred to as the market closest to the ideal of perfect competition, notwithstanding currency intervention by central banks. According to the Bank for International Settlements,the preliminary global results from the 2013 Triennial Central Bank Survey of Foreign Exchange and OTC Derivatives Markets Activity show that trading in foreign exchange markets averaged $5.3 trillion per day in April 2013. This is up from $4.0 trillion in April 2010 and $3.3 trillion in April 2007. Foreign exchange swaps were the most actively traded instruments in April 2013, at $2.2 trillion per day, followed by spot trading at $2.0 trillion. According to the Bank for International Settlements,as of April 2010, average daily turnover in global foreign exchange markets is estimated at $3.98 trillion, a growth of approximately 20% over the $3.21 trillion daily volume as of April 2007. Some firms specializing on foreign exchange market had put the average daily turnover in excess of US$4 trillion. The $3.98 trillion break-down is as follows:
$1.490 trillion in spot transactions
$475 billion in outright forwards
$1.765 trillion in foreign exchange swaps
$43 billion currency swaps
$207 billion in options and other products
After 1973
The year 1973 marks the point to which nation-state, banking trade and controlled foreign exchange ended and complete floating, relatively free conditions of a market characteristic of the situation in contemporary times began (according to one source), although another states the first time a currency pair were given as an option for U.S.A. traders to purchase was during 1982, with additional currencies available by the next year .On 1 January 1981, as part of changes beginning during 1978, the People's Bank of China allowed certain domestic "enterprises" to participate in foreign exchange trading. Sometime during the months of 1981 the South Korean government ended forex controls and allowed free trade to occur for the first time. During 1988 the countries government accepted the IMF quota for international trade.
Intervention by European banks especially the Bundesbank influenced the forex market, on February the 27th 1985 particularly. The greatest proportion of all trades world-wide during 1987 were within the United Kingdom, slightly over one quarter, with the U.S. of America the nation with the second most places involved in trading.
During 1991 the republic of Iran changed international agreements with some countries from oil-barter to foreign exchange.
Market size and liquidity
Main foreign exchange market turnover, 1988–2007, measured in billions of USD.
The foreign exchange market is the most liquid financial market in the world. Traders include large banks, central banks, institutional investors, currency speculators, corporations, governments, other financial institutions, and retail investors. The average daily turnover in the global foreign exchange and related markets is continuously growing. According to the 2010 Triennial Central Bank Survey, coordinated by the Bank for International Settlements, average daily turnover was US$3.98 trillion in April 2010 (vs $1.7 trillion in 1998) . Of this $3.98 trillion, $1.5 trillion was spot transactions and $2.5 trillion was traded in outright forwards, swaps and other derivatives.
In April 2010, trading in the United Kingdom accounted for 36.7% of the total, making it by far the most important centre for foreign exchange trading. Trading in the United States accounted for 17.9% and Japan accounted for 6.2%.
In April 2013, for the first time, Singapore surpassed Japan in average daily foreign-exchange trading volume with $383 billion per day. So the rank became: the United Kingdom (41%), the United States (19%), Singapore (5.7)%, Japan (5.6%) and Hong Kong (4.1%).
Why Trade Forex With OTL Trading ?
Tight Spread & Minimum Commision
OTL Trading pride ourselves on having Minimum commissions and tightest dealing spreads on FOREX products, whilst maintaining our quality service. We strive to differentiate ourselves from other FOREX brokers by offering the best online FOREX trading platform.
Flexible Margin Requirements
FOREX traders can benefit from some of the lowest margin requirements in the industry, meaning customers will only have to deposit a small percentage of the total notional value of the trade when looking to open new positions.Interst/Swap Free Account Facility Also AKA Sharia Account
The OTL Trading Sharia account, is designed for traders who cannot receive or pay swaps for religious reasons. The trading account is compliant with Sharia law enabling traders to take advantage of OTL Trading's cutting edge trading technology and deep liquidity24-Hour Live Online Support
At OTL Trading we recognise the importance of clients being able to access their account and trade whenever they want, wherever they are, particularly when market prices are moving quickly. We therefore provide our clients unrestricted access to their account 24 hours a day, 5 days a week via the Vtx software available for download.OTL Trading Offer FOREX Products
We are offering major Currencies, Cross currencies & Precious MetalCurrencies
EUR/USDGBP/USD
USD/JPY
USD/CHF
AUD/USD
USD/CAD
Crosses
EUR/GBPEUR/JPY
EUR/CHF
GBP/JPY
Metal
XAU/USD ( GOLD )XAG/USD (SILVER )
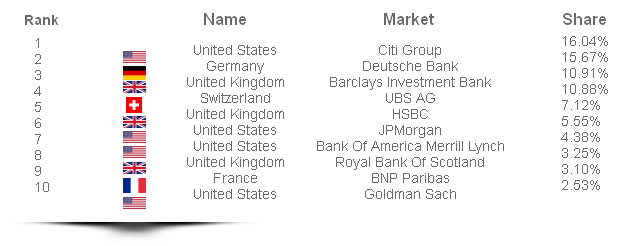
Top 10 currency traders
% of overall volume, May 2014
There are few markets that require the level of privacy, honesty, and trust between its participants as the FX market. This creates great obstacles for traders, investors, and institutions to overcome as there is a lack of transparency. With little to no transparency trader’s ability to verify transactions becomes virtually impossible. Without transparency there is no trust between the client and the broker.
Our Clients (hereinafter known as "THE CLIENT" or simply You) are the most important part of our business, and we work tirelessly to ensure your complete satisfaction. Protecting the privacy and safeguarding the personal and financial information of our clients and website visitors is one of our highest priorities
This privacy policy sets out how OTL Trading uses and protects any information that you give OTL Trading when you use this website.
OTL Trading is committed to ensuring that your privacy is protected. Should we ask you to provide certain information by which you can be identified when using this website, then you can be assured that it will only be used in accordance with this privacy statement.
All client's funds deposited with OTL Trading are fully segregated from the company’s funds and are kept in separate accounts. This ensures that those funds belonging to clients cannot be used for any other purpose. We maintain sufficient liquid capital to cover all client deposits, potential fluctuations in the company’s currency positions and outstanding expenses. We use rigorous firewalls and Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) software to protect information during transmission. All deposited funds are safely kept on a separated account with the purpose of ensuring the protection of a client money.
OTL Trading uses an automated transaction monitoring and risk-management system to ensure that a client's balance will never fall below the level of their initial deposits, protecting them from any losses beyond their original investment at OTL Trading’s cost.
Risk Disclaimer:- Trading foreign exchange on margin carries a high level of risk, and may not be suitable for all investors. Past performance is not indicative of future results. The high degree of leverage can work against you as well as for you. Before deciding to invest in foreign exchange you should carefully consider your investment objectives, level of experience, and risk appetite. The possibility exists that you could sustain a loss of some or all of your initial investment and therefore you should not invest money that you cannot afford to lose. You should be aware of all the risks associated with foreign exchange trading, and seek advice from an independent financial advisor, legal advisor, friends and close family members if you have any doubts




